Summary
Constructor
java
class Thing {
double num;
Thing() {
// initialise the instance
this.num = 1; // modifying instance fields
}
}
Instantiation
java
Thing thing = new Thing(); // creates new instance and runs the constructor
Information hiding
- prevents the user from accessing methods/fields from outside
java
class Thing {
private double num; // private field
public void func() {
this.num = 0; // still possible to modify private fields internally
}
}
Thing thing = new Thing();
thing.num = 0; // not possible due to private keyword
thing.func(); // possible since the method is public
Class methods and class fields
- methods/fields that are associated with the class and not just any one instance
java
class Thing {
static double count; // class field
public void func() {
Thing.count = 0; // modifying class fields interanally
}
}
Thing.count = 0; // modifying class fields externally
Final fields
- makes fields immutable, their value can only be set on declaration or in the constructor
java
class Thing {
final zero = 0; // immutable field
}
Concept
Encapsulation
- packaging of relevant variables and methods(verbs) in an object(nouns)
java
class Thing {
int a; // instance fields
int fun() { // instance methods
return 1;
}
}
Fields
- variables associated with an instance of an object
Methods
- functions associated with an instance of an object
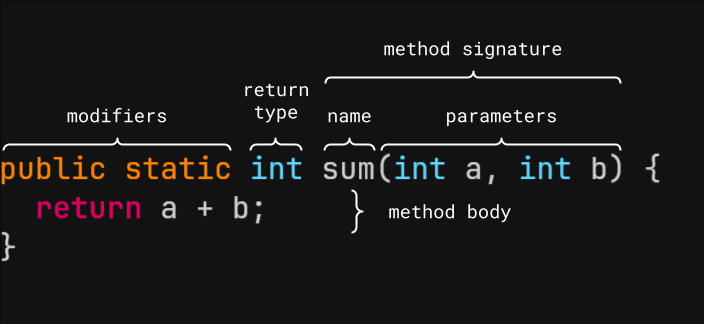
Tell, don’t ask
- avoid accessors(getters) and mutators(setters)
- instead of the user getting the values and then performing the calculation externally, we implement a function that can do the calculation internally
Composition
- “has-a” relationship
- using other classes within a class
- ie. Point class to represent the centre in a Circle class
Abstraction barrier
- Implementer -> provides the implementation of the function
- Client -> uses the functions/classes to perform a task
- the client would not care about the specific imlementation of the function, just that it performs the desired task
- the implementer has the freedom to change the implementation, as long as the behaviour remains unchanged
Application
Main method, entry point
java
class Thing {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// do something
}
}
Circle class
java
import java.lang.Math;
class Circle {
private int x; // instance fields
private int y;
private int r;
public static int count = 0;
public Circle(int x, int y, int r) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.r = r;
Circle.count++;
}
public double getArea() {
return Math.PI * this.r * this.r;
}
}