counting II
Complete
Succeeds: counting
Summary
Counting methods
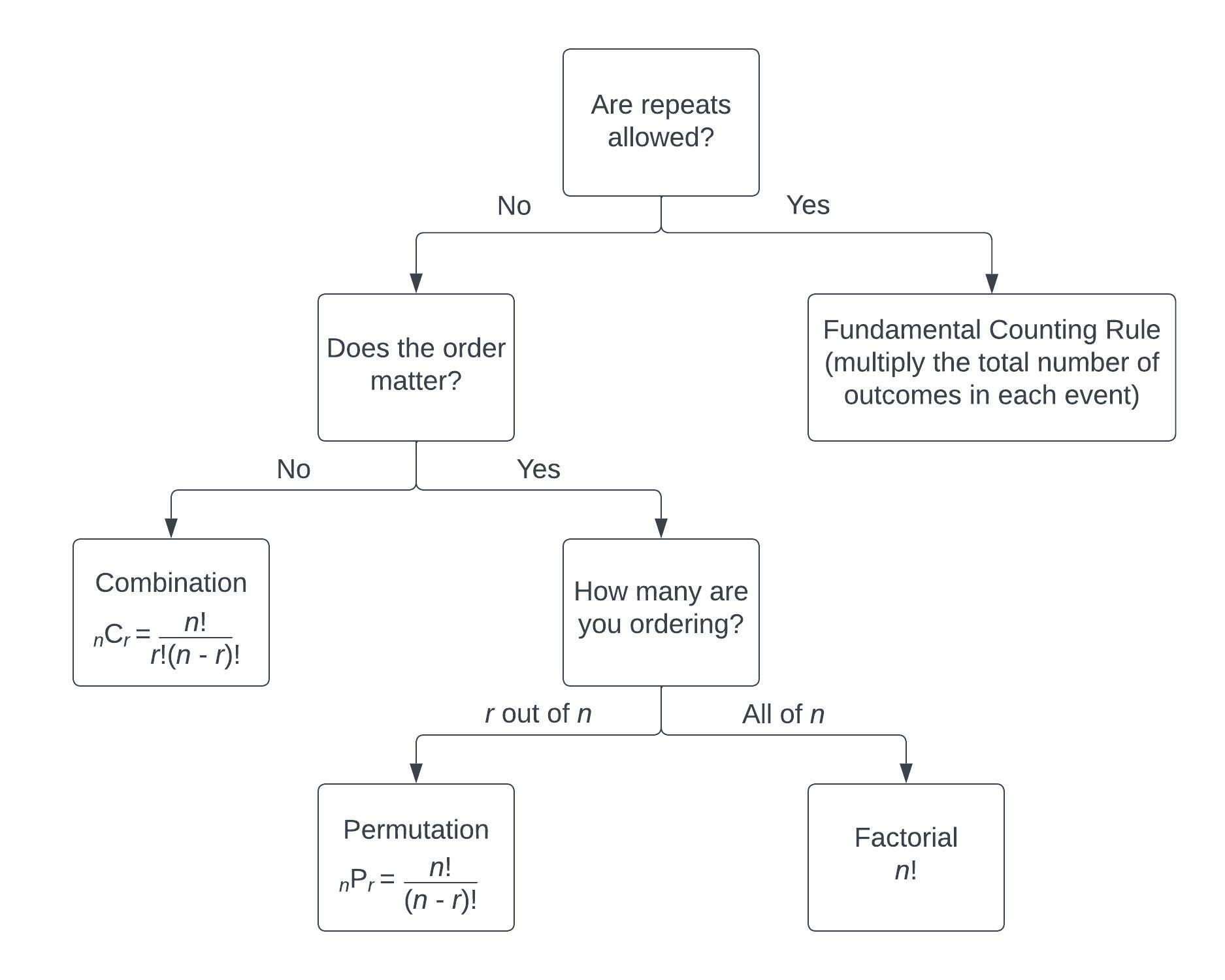
Concept
Multiplication principle
- counting the number of outcomes from experiments performed sequentially
Addition principle
- counting the number of independent outcome types
Permutation
- number of ways to arrange
Combination
- number of ways to choose
Application
Forming odd 3-digit numbers without repetition
multiply within a group of outcomes, add between groups
Divide into smaller problems
- How many ways can 6 persons line up to get on a bus, if 3 persons insist on following one other?
- Consider the digits 0,1,2,3,4,5 and 6. If each digit can be used at most once, how many 3-digit numbers, which are equal to or greater than 301, can be formed
- How many ways can 4 men and 3 women sit in a row if no two women are allowed to sit together?
Two dice(unordered)