orders of growth
Summary
Common orders of growth
Adding orders of growth
See recurrence relations for orders of growth in recursive functions
Concept
Rough measure of resources(time and space) used by a computational process, with respect to the problem size
OOG is an abstraction technique, ignoring details that seem to be irrelevant/external to the program
Let n denote the size of the problem, and let r(n) denote the resource needed solving the problem of size n
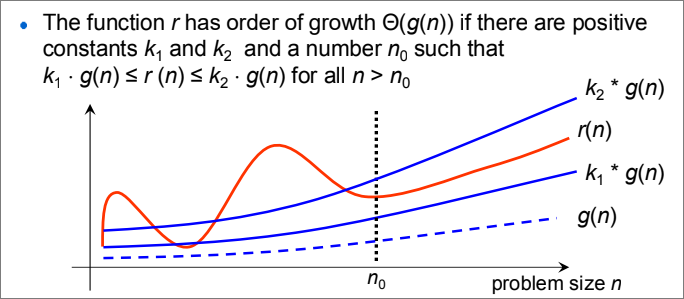
Big Theta Notation
describes BOTH the upper and lower bound of a function, sometimes referred to as the average time complexity
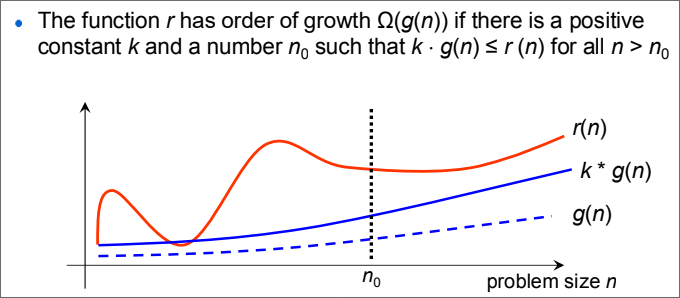
Big Omega Notation
describe the asymptotic lower bound of an algorithm, or its best-case scenario
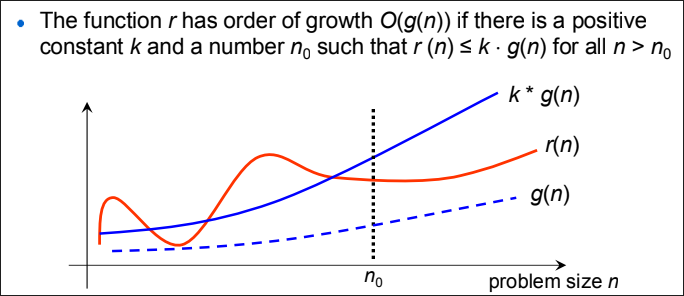
Big O Notation
describe the asymptotic upper bound of an algorithm, or its worst-case scenario
Also minor terms, ie. in
, and are not relevant since we can choose to overrule them
Application
Recursive functions
const f = x => x === 1 ? x : f(x - 1); // T(n-1) + O(1)
const f = x => x === 1 ? x : f(x / 2); // T(n/2) + O(1)
for(let i = 0; i < n; i = i + 1) // T(n-1) + a
for(let i = 0; i < n; i = i * 2) // T(n/2) + a
for(let i = 0; i < 100 * n; i = i + n) // a
for(let i = 0; i< n * n; i = i + n) // T(n-1) + a